04.02.2025
Back pain
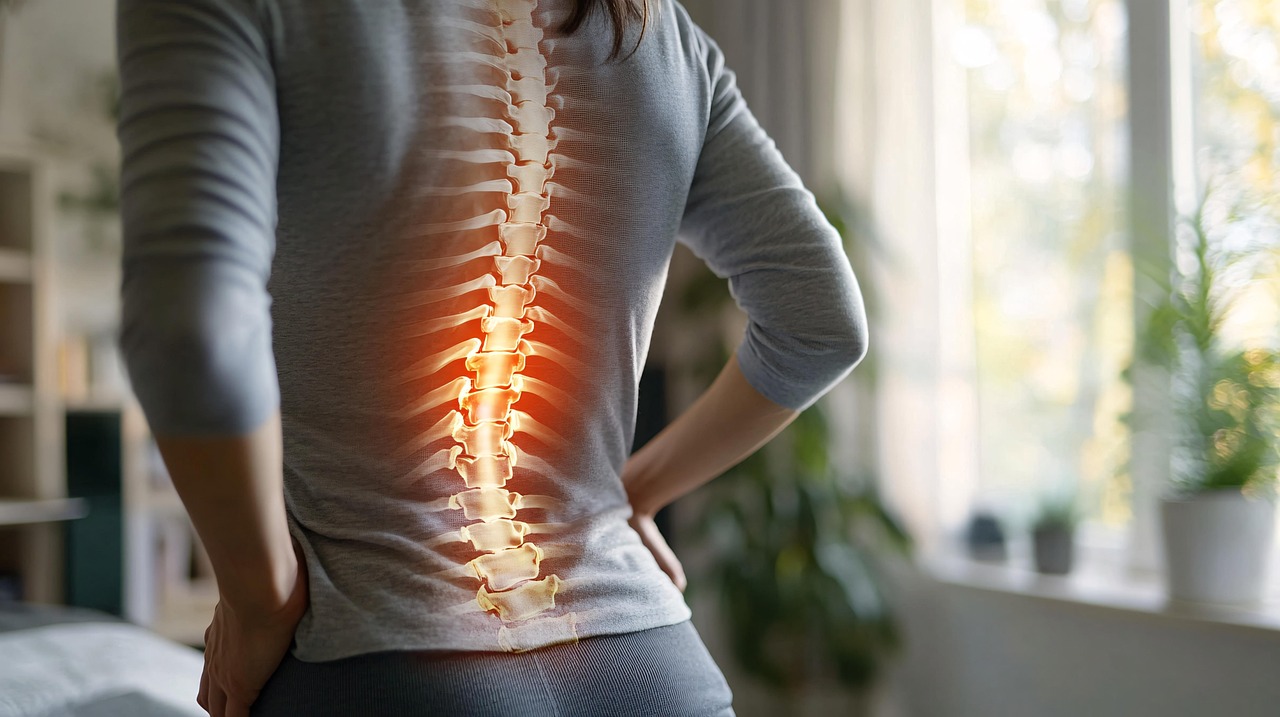
Back pain, most commonly in the lower back, is difficult to avoid in the modern world. Many jobs require long periods of sitting or similar activities which can put pressure on the ack. These types of pain can vary, they can be blunt and constant, or rather sharp and sudden. Still, there are ways to alleviate the symptoms and avoid further injury.
Back pain is one of the most common health issues, studies suggest that 8 in 10 people have problems with back pain during their lifetime. Studies also suggest that 23% of adults around the world suffer from chronic lower back pain. Acute back pain is sudden and often lasts between a few days and a few weeks, while chronic back pain lasts more than three months.
You can find more information about chronic pain here (link).
Back pain can be caused by a multitude of factors, physical trauma, problems in any part of the spine, degeneration of the musculoskeletal system brought on by aging or other pathologies, the effects of cancer, infections, inflammations, metabolism of bone tissue, bad posture or even because of psychiatric conditions.
Understanding the causes of pain early on is key to effective treatment. A thorough history of the symptoms as well as a physical examination are necessary. Acute back pain is usually caused by trauma or sudden changes in some other pathological condition. Chronic pain is often connected to longer-lasting conditions and causes.
Other information concerning the pain, like the type of pain, specific localization, and stimuli that worsen or better the pain, can be critical in formulating an efficient treatment plan.
Improvements in the general physical condition of the individual can do a lot to prevent back pain. Strengthening back muscles and education on how to properly use them can play a key role in this problem. Different exercises can in many ways improve the strength and endurance of the back. Walking, cycling or swimming can be a good choice for aerobic exercises which don’t put a lot of strain on the back and so don’t carry much risk. Exercises that focus on the back and abdominal muscles help better functioning and lessen the strain on the back. Lesser body weight also helps, excess weight can stress the back. Changes in lifestyle, such as higher levels of physical activity, proper posture, correct lifting techniques, a healthy diet, or quitting smoking, can all help in the prevention and regulation of back pain symptoms.
If the pain is present for longer periods of time or is intense you shouldn’t consider exercising without consulting a healthcare professional.
Sometimes back pain can pass all by itself, in case it doesn’t improve in the span of a few weeks it is necessary to visit a doctor. A visit to the doctor is also needed if you notice other symptoms accompanying back pain, these are:
- Numbness and tingling
- Intense pain which is unresponsive to medication
- Pain after a fall or injury
- Pain accompanied by urinary problems, weakness, numbness or pain in the legs, a fever, and unexpected weight loss.
*This text is intended for informational purposes only. If you experience any symptoms, it is recommended that you seek advice from your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional.*
*Image taken from the site: https://pixabay.com/illustrations/ai-generated-back-back-pain-pain-9146625/
Branch, N. S. C. a. O. (2025, January 8). Back pain. National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/back-pain
Casiano, V. E., Sarwan, G., Dydyk, A. M., & Varacallo, M. A. (2023, December 11). Back pain. StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538173/
How to manage low back pain before it gets worse | NIH MedlinePlus Magazine. (n.d.). NIH MedlinePlus Magazine. https://magazine.medlineplus.gov/article/how-to-manage-low-back-pain-before-it-gets-worse
Your trusted partner in finding medical information. We offer access to reliable resources and make it simple for you to get in touch with qualified medical service providers. Our goal is to assist you in achieving optimal health through dependable information and ongoing support, whether it's advice, a physical examination, or expert consultation.